EFS (Encrypting File System) is a built-in component of the NTFS file system, which comes with all professional versions of Windows since Windows 2000. Using EFS, you can encrypt files and folders so that only authorized logged-on users can view the data. If someone else logs in with unauthorized users, or boots from a Windows PE or Linux CD, or removes the hard drive, the files remain encrypted and they are inaccessible.
To use EFS, you simply change the property of a folder and enable encryption. Once a folder is encrypted with EFS, all the files you create within that folder or move into that folder are automatically encrypted.
How to Encrypt Your Files with EFS in Windows?
Select one or multiple files and folders in Windows Explorer, right-click the selection afterwards and select Properties from the context menu.
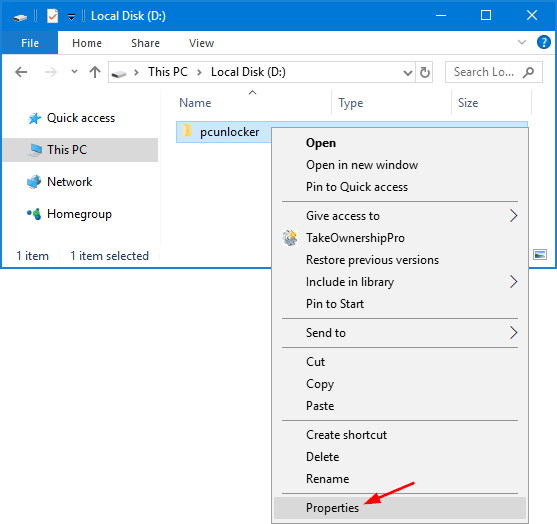
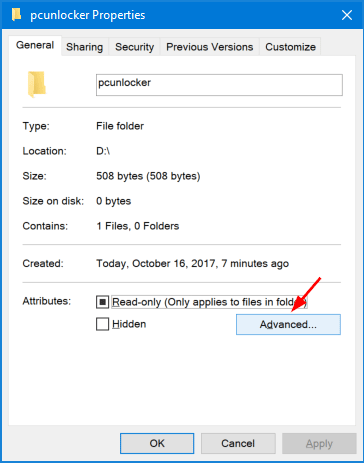
Click on Advanced button from the Properties window.
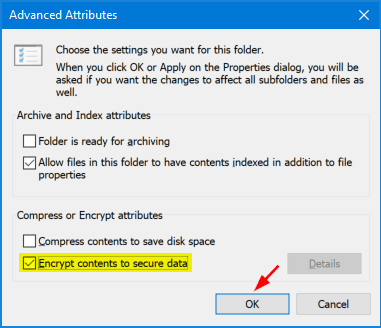
Tick the Encrypt contents to secure data checkbox on the new window, and click OK.
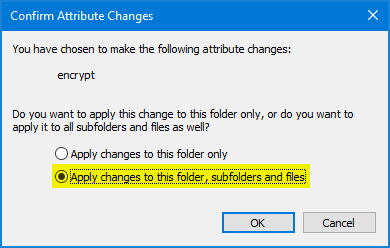
If you have selected at least one folder, you will be asked if you only want to encrypt the root files of that folder, or files in sub-folders as well.
The files and folder in question are then displayed in green in Windows Explorer. Congratulations, you have just encrypted your first files or folders with EFS.
Note: If the original EFS certificate is lost or corrupted in your system, you’ll lose access to your EFS encrypted files. It is important to backup your EFS certificate in a safe location.
Conclusion
Because it is already included in a typical Windows installation, EFS is the quickest way to encrypt your files if you’re already using Windows. There’s nothing to download or install and encrypting a folder can be done with just a few clicks. Unless you really have very sensitive information that requires a very strong encryption solution, EFS should suffice.