How can I change domain password from command line? Have you forgotten domain administrator password? In this tutorial we’ll show you 4 ways to reset domain admin password on Windows Server 2008 domain controller.
Method 1: Reset Domain Admin Password Using Active Directory Users and Computers snap-in
- Click the Start button, and then select All Programs > Administrative Tools > Active Directory Users and Computer.
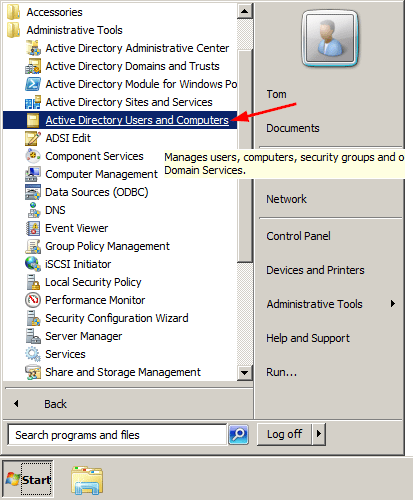
- When the Active Directory Users and Computers MMC snap-in opens, expand your domain and click Users in the left pane.
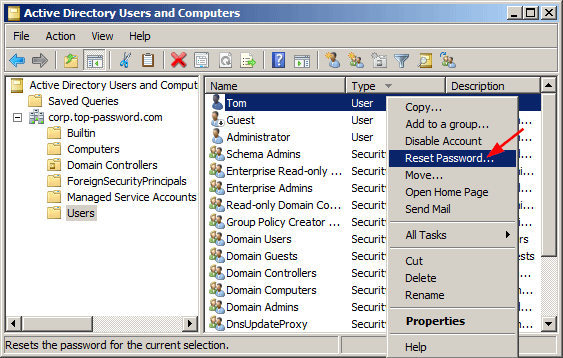
- In the right pane, right-click the name of the account, and click Reset Password.
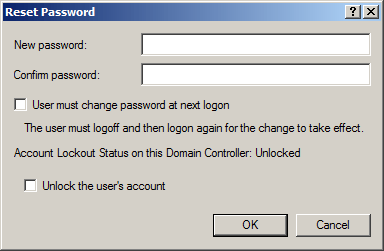
- Type and then confirm the new password. Click OK.
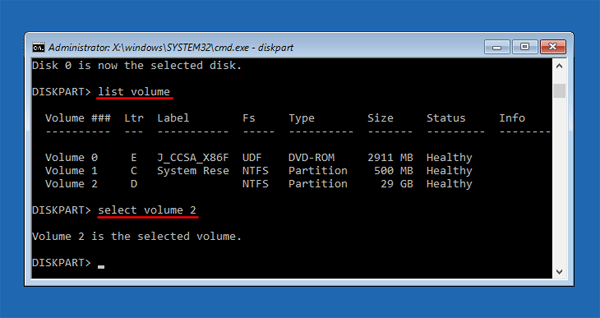
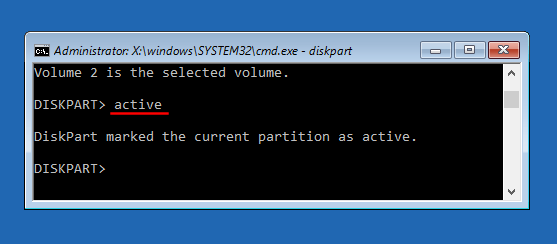
Method 2: Reset Domain Admin Password from Command Line
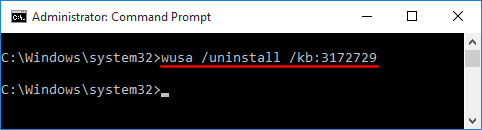
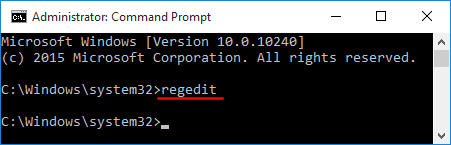
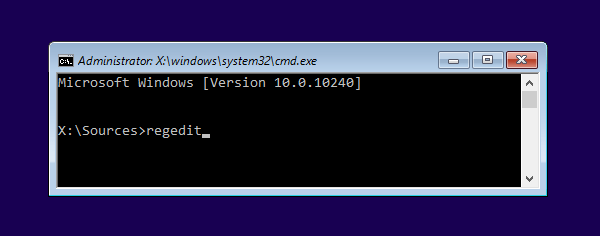
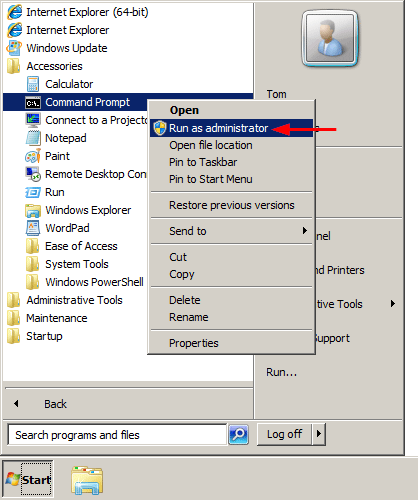
- To get started, you need to open an elevated Command Prompt. Click the Start button, and then select All Programs > Accessories. Right-click on Command Prompt and select Run as administrator.
- At the Command Prompt, you can run the net user user_name new_password /domain command to change your domain user password. For example, if you wan to change the password of the user Tom to P@ssword123, run the below command:
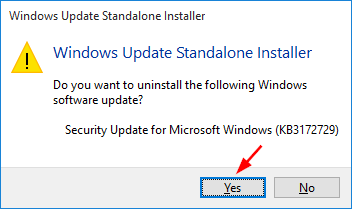
net user Tom P@ssword123 /domain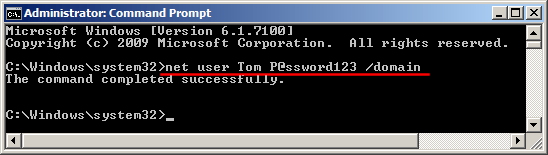
- Now you’ve successfully reset your domain administrator password from command line.
Method 3: Reset Domain Admin Password by Pressing Ctrl+Alt+Del
- When you’re logged into Windows Server, press the Ctrl+Alt+Del key combination, you will still see this task menu. Click Change a password.
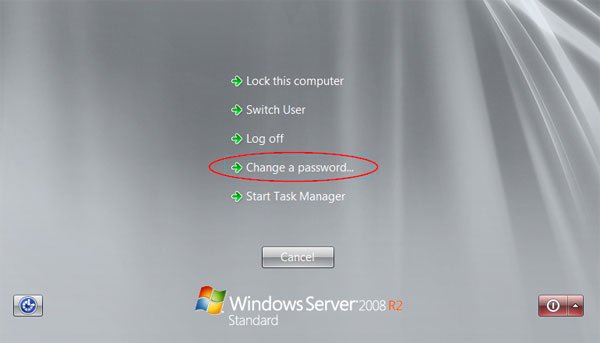
- Type your old password followed by a new password as indicated, and then type the new password again to confirm it. Press Enter or click on the blue arrow pointing right.
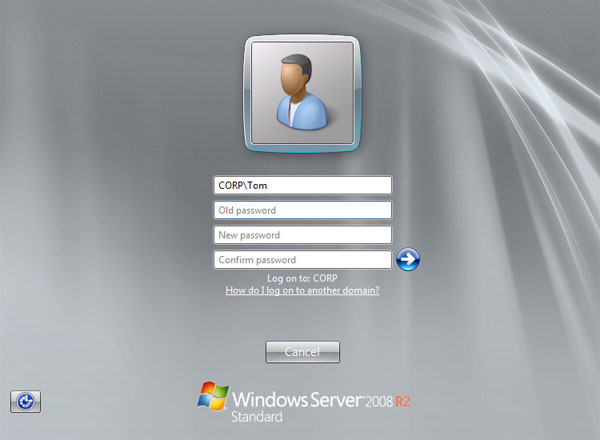
- You should then receive a message stating that you have successfully changed your password.
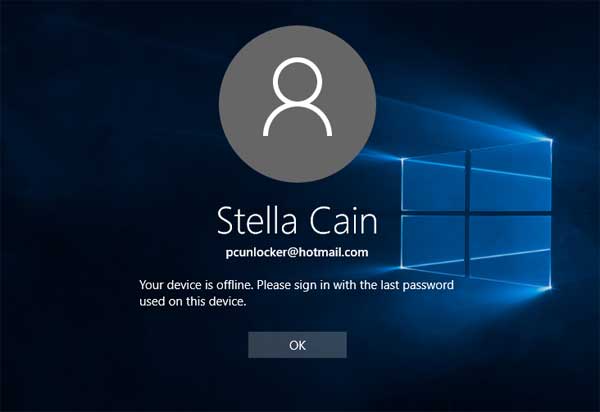
Method 4: Reset Domain Admin Password Using PCUnlocker
- Download PCUnlocker Enterprise (distributed as .zip format) and save it to your desktop. When the download is complete, right-click on the .zip file to extract it.
- After extracting, burn the PCUnlocker ISO file to your USB flash drive using ISO2Disc – an excellent utility that helps to create bootable CD/USB flash drive from ISO file.
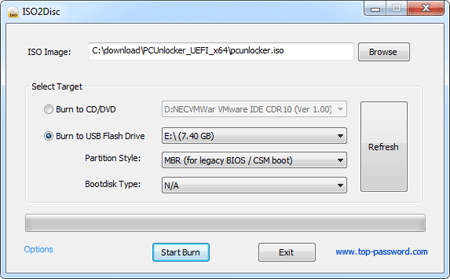
- Next insert the USB flash drive into your Windows Server machine. Restart the server and enter into BIOS Setup: set the USB as first boot device. After booting from USB, it’ll take you to the PCUnlocker application.
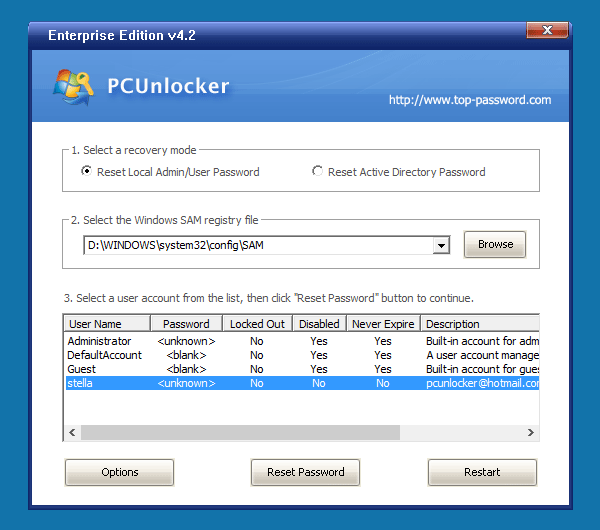
- Switch the recovery mode to Reset Active Directory Password. The program will display your domain accounts stored in the Active Directory database. Choose an user and click Reset Password.
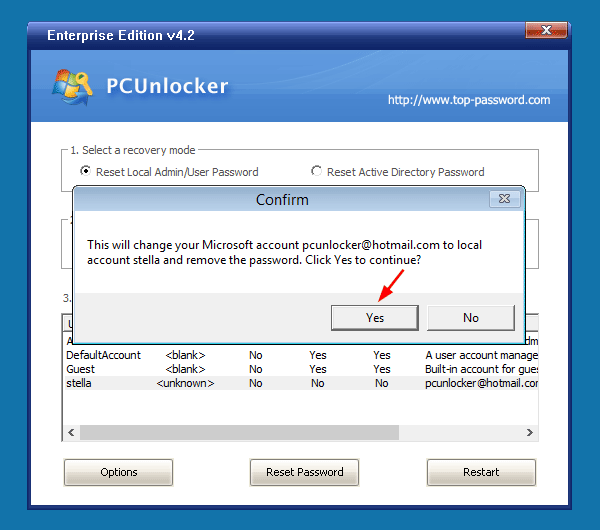
- Click Yes to confirm and your domain user password will be changed to Password123 immediately.
Reboot the server without USB, you can then log in to Windows Server 2008 domain controller successfully. That’s it!