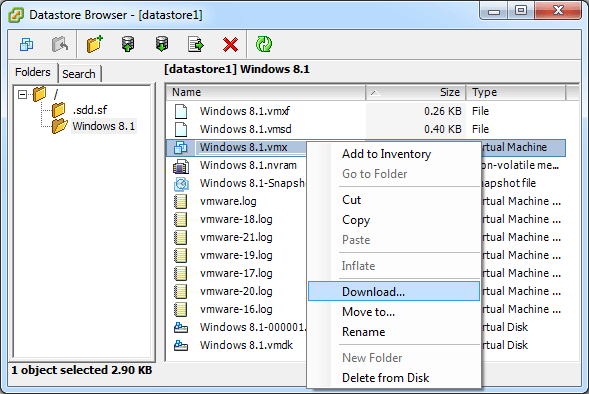
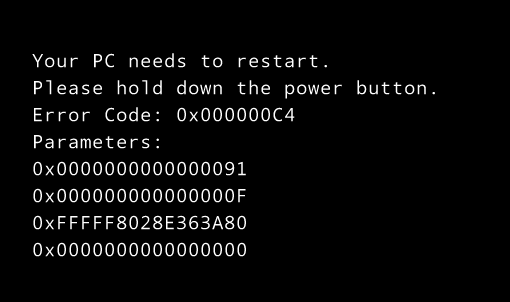
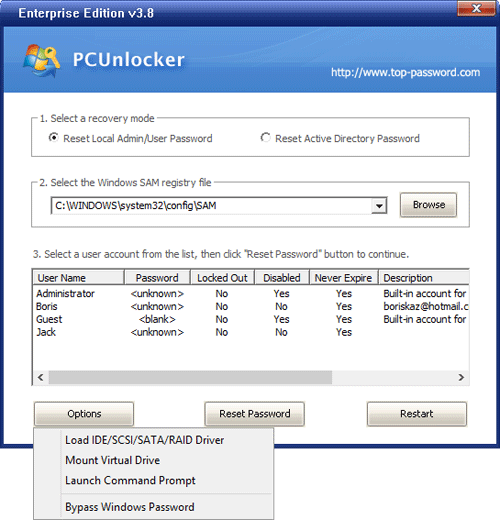
When VMware released ESXi 4.0, they officially supported booting your OS drive from a paravirtual SCSI controller. Comparing to BusLogic and LSI Logic, Paravirtual SCSI (PVSCSI) controllers are high-performance storage controllers that can result in greater throughput and lower CPU utilization. However, since Windows doesn’t have native driver for the VMware PVSCSI adapter, you will find that a paravirtualized hard disk can’t be recognized during Windows installation or booting from WinPE.
To fix this problem you need to grab the pvscsi driver and add it to your WinPE bootdisk, or load the driver on the fly. But it’s not easy to extract pvscsi boot floppy images from VMware ESXi. Lucikly I came across a floppy disk image called pvscsi_windows2008.flp under my VMware Workstation installation directory: C:\Program Files (x86)\VMware\VMware Workstation\Resources.
For your convenience, we load the pvscsi-Windows2008.flp image in our virtual floppy drive and then archive the setup files in both .iso and .zip formats. Below you can download pvscsi driver for VMware Paravirtual SCSI in different formats:
- Floppy disk image: Click here
- ZIP archive: Click here
- ISO image: Click here