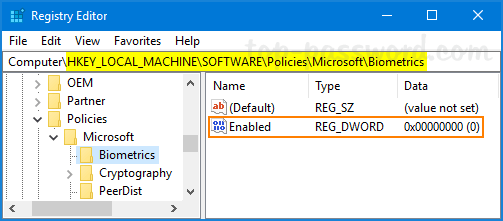
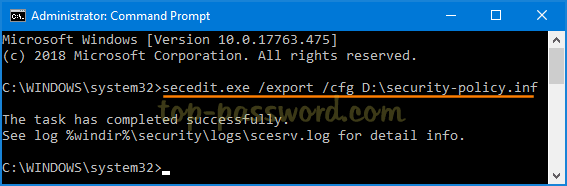
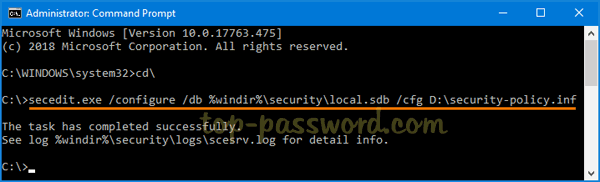
Unable to re-activate windows 10 after hardware change? If your Windows 10 was activated with a digital license instead of product key, you can link the digital license to your Microsoft account so you can easily re-activate Windows 10 after upgrading or replacing hardware. No need to contact Microsoft Activation Centers and explain your situation.
Part 1: Link Windows 10 Digital License to Microsoft Account
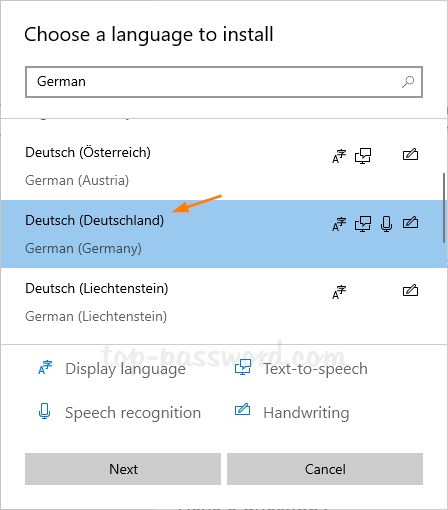
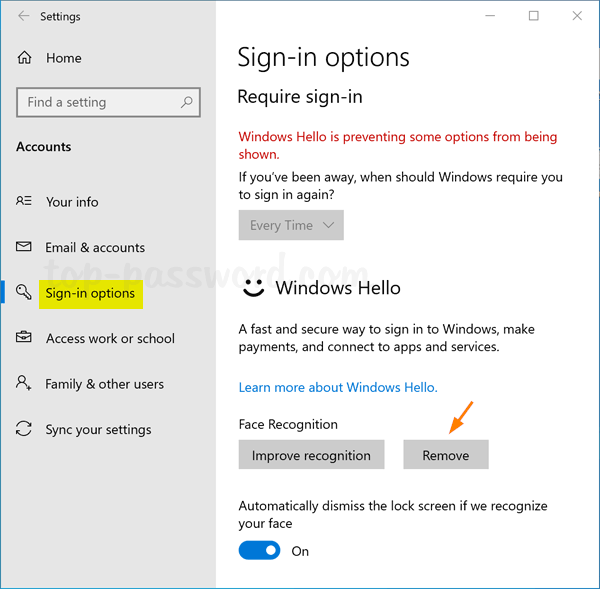
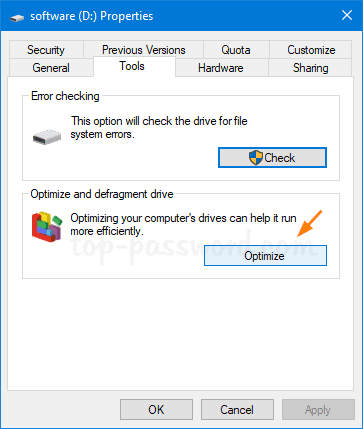
- Open the Settings app, and then click on Update & Security.
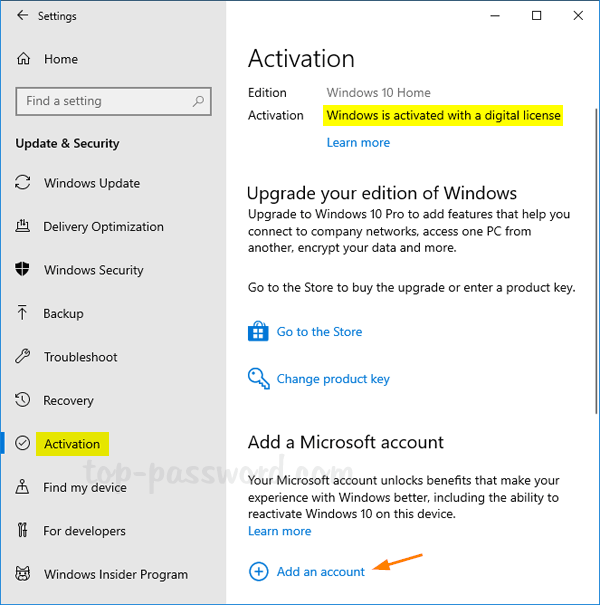
- Select the Activation tab on the left side. If you have a digital license, you’ll see the activation status message “Windows is activated with a digital license” on the right pane. To link the digital license to your Microsoft account, click on Add an account.
- When the Sign-in page appears, enter your Microsoft account email address and click Next. Afterwards, enter your Microsoft account password.
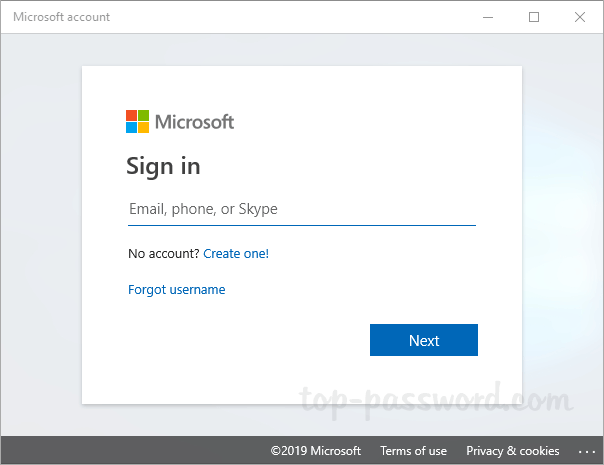
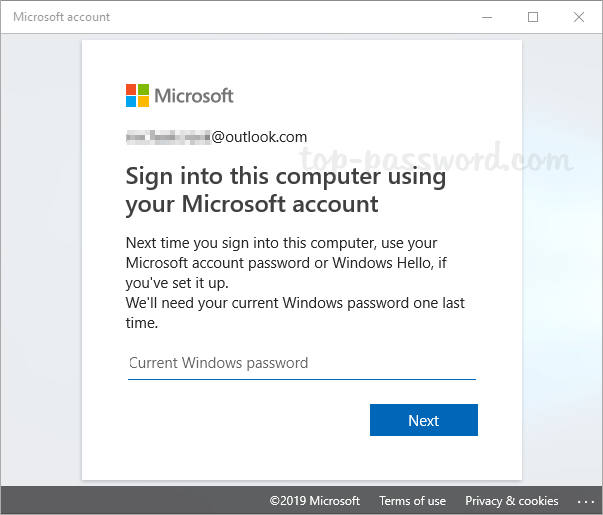
- Next, you’ll be prompted to switch from local account to Microsoft account. Enter the local account password, and click Next.
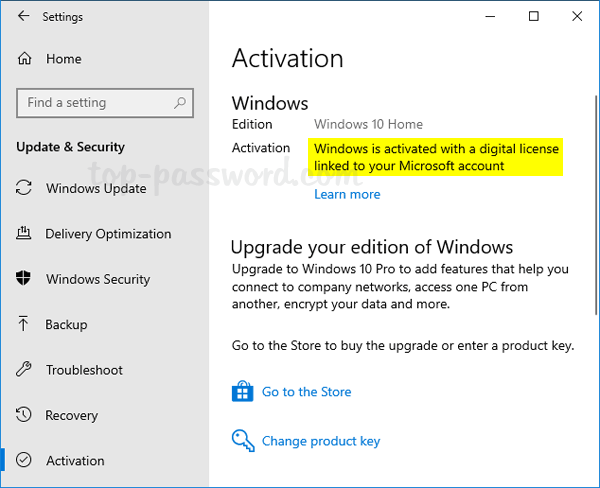
- If your account was successfully linked, the activation page will now display “Windows is activated with a digital licensed linked to your Microsoft account“.
When you use a Microsoft account to sign in to Windows 10, the digital license will be automatically linked to your Microsoft account, without having to go through the above procedure.
Part 2: Re-activate Windows 10 After Hardware Change
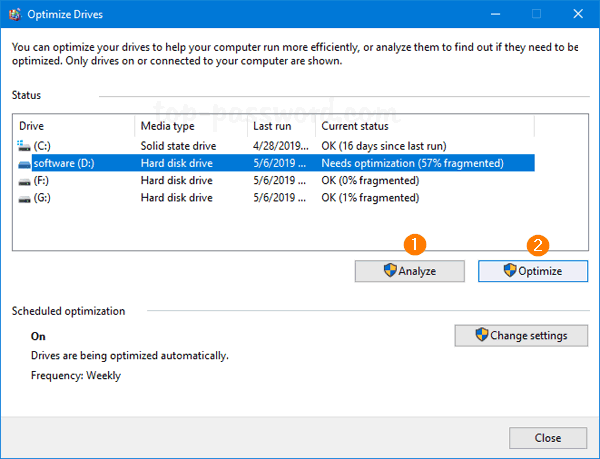
A significant hardware change can cause Windows 10 to lose its activation. If you’ve got the digital license linked to your Microsoft account before hardware change, you can now run the Activation Troubleshooter to re-activate your Windows 10 with ease.
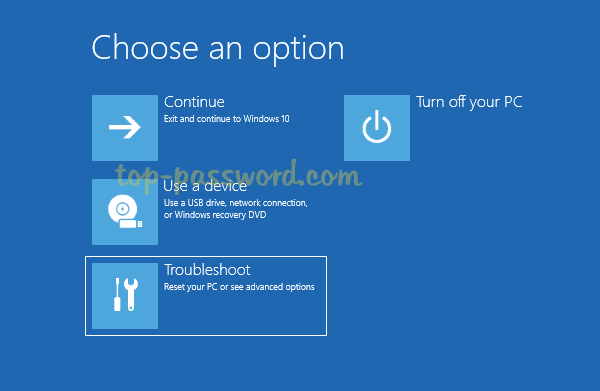
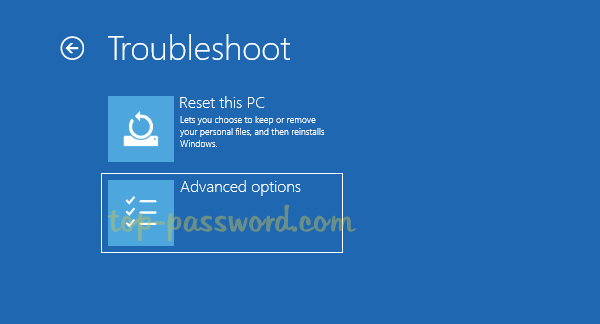
- Open the Settings app and navigate to Update & Security -> Activation. On the right side, click on Troubleshoot.
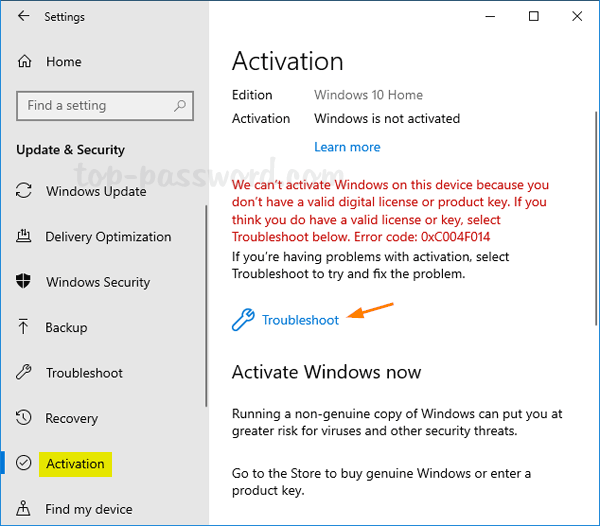
- The Activation Troubleshooter will scan your computer hardware and attempt to activate Windows. If that fails, click the option “I changed hardware on this device recently“.
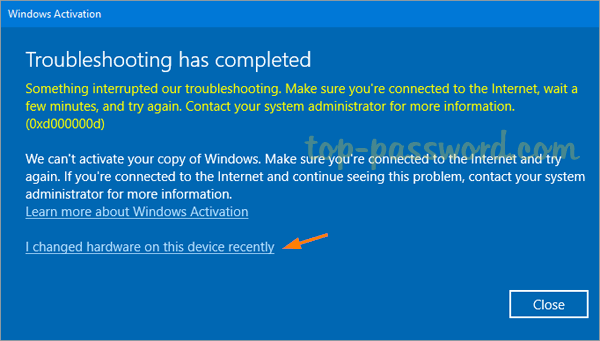
- You’ll be prompted to sign in with your Microsoft account. Just select your Windows 10 PC from the device list, check the box labeled “This is the device I am using right now“, then click on Activate to assign the digital license to your current computer.
Conclusion
Linking Windows 10 digital license to Microsoft account could make activation easier after hardware change. If you forgot to link the digital license and unable to re-activate your Windows, you may need to contact Microsoft with a proof of purchase and explain that you’ve upgrade the hardware on your computer.