How can I find out when a user account was created in Active Directory? Is there a way to list all AD users created in the last 30 days? It’s vitally important to monitor user account creations in order to reduce the risk of security breaches. In this tutorial we’ll show you different ways to find when a specific AD user was created, and list all recently created accounts in Active Directory.
Part 1: Find the Creation Date of Specific AD User
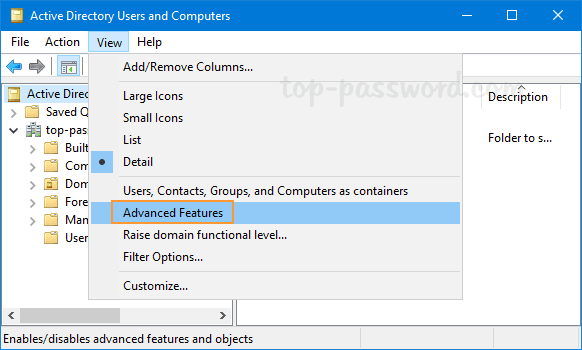
- In Active Directory Users and Computers snap-in, click on the View menu and select Advanced Features.
- Expand the domain and choose Users in the left-hand pane, you’ll see a list of AD users. Right-click on the account for which you want to find out the creation date, and select Properties.
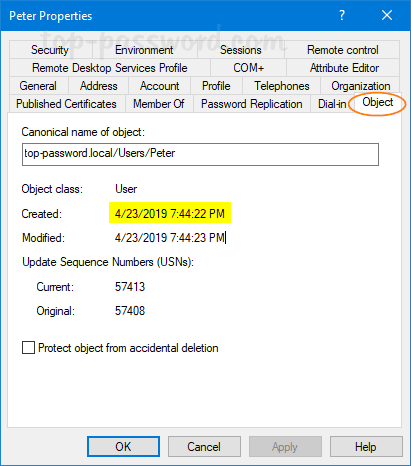
- Go to the Object tab and you can view the date and time when the account has been created.
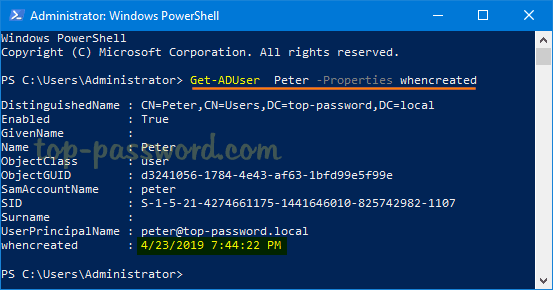
Additionally, you can also find out the user account creation date using PowerShell. Just type the following command and hit Enter.
Get-ADUser your_username -Properties whenCreated
Part 2: List All Recently Created Accounts in Active Directory
When you need to find a list of users created in Active Directory in the last 30 days, just open PowerShell with elevated privileges and execute the below commands:
$DateCutOff = (Get-Date).AddDays(-30)
Get-ADUser -Filter * -Properties whenCreated | where {$_.whenCreated -gt $DateCufOff} | FT Name, whenCreated
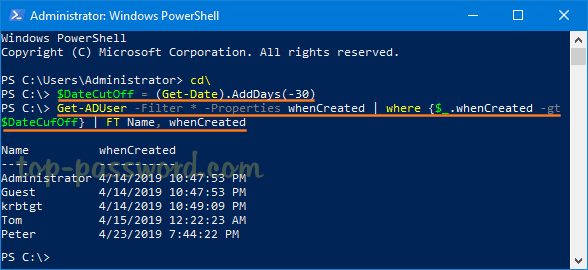
The first command uses the AddDays method to minus 30 days from the current date, while the second command pulls only accounts created after a certain date stored in $DateCutOff.