How can I open Folder Options through the Command Prompt? If you want to show hidden files or customize how your files are displayed in Windows Explorer, you have to access Folder Options. In this tutorial we’ll show you 4 quickest ways to open Folder Options in Windows 11, 10, 8 and 7.
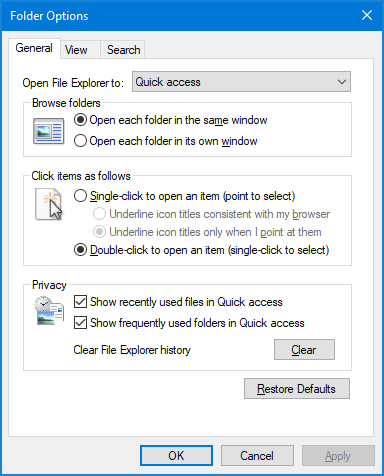
Method 1: Open Folder Options from Windows Explorer
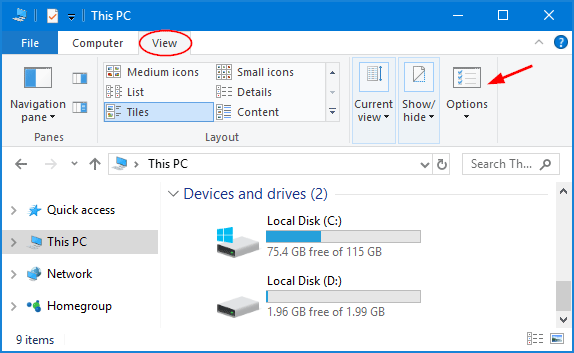
Press WIN + E keyboard combination to open Windows Explorer (also known as “File Explorer). Click the View tab, and then click Options in the ribbon. This will open Folder Options dialog.
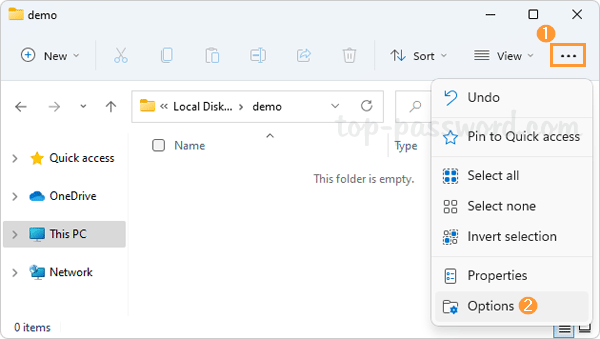
In Windows 11, open File Explorer and click on the See more button (three dots) on the right side of the toolbar, and then select Options.
Method 2: Open Folder Options from Control Panel
Open the Control Panel. Change the View by option to Large icons or Small icons.
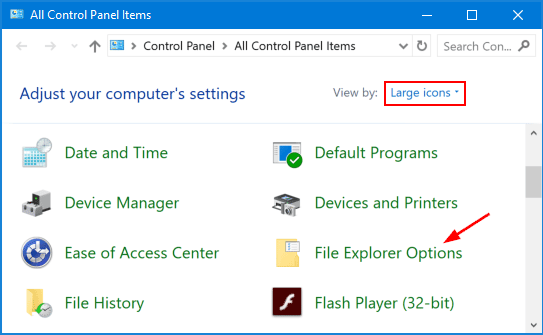
Click File Explorer Options to open Folder Options.
Method 3: Open Folder Options from Run or Command Prompt
Press the WIN + R keys together to open the Run command box, and then type control.exe folders and press Enter to access Folder Options.
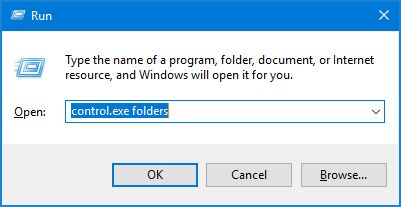
If you’re at Command Prompt, type control.exe folders and you can also access Folder Options quickly.
Method 4: Open Folder Options by Search
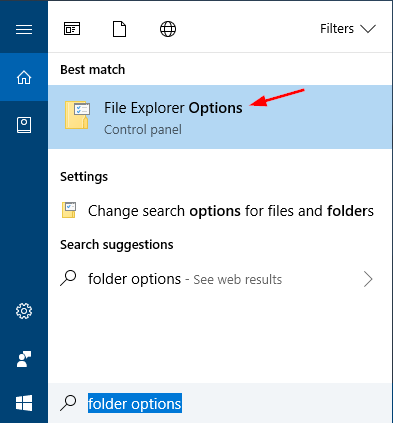
If you’re running Windows 10/8, type folder options into the Cortana Search box on the taskbar. Click on File Explorer Options from the result.
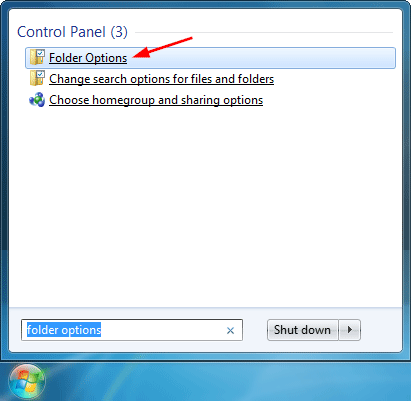
If you’re running Windows 7, click the Start button and type folder options into the search box, then click Folder Options.
That’s it!