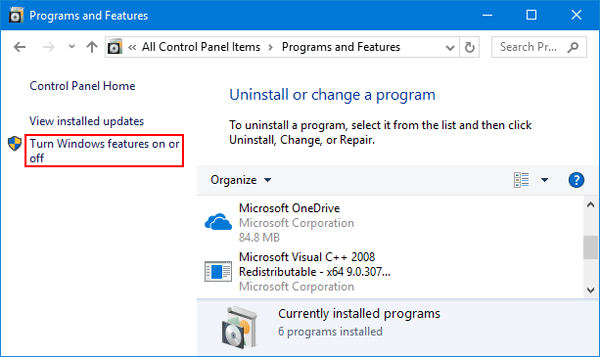
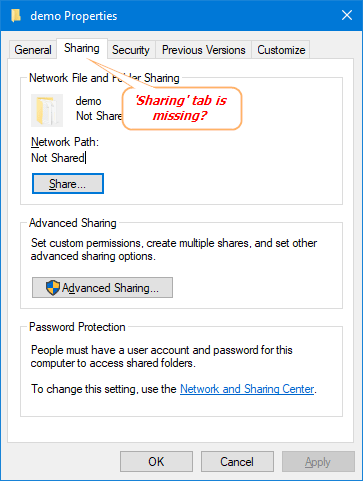
Sharing tab missing in Folder Properties on Windows 10? If you want to share a folder with other users, just right-click on the folder and select Properties, and then go to the Sharing tab in the Folder Properties window. Sometimes you might find the Sharing tab goes missing. In this tutorial we’ll enable or disable Sharing tab in Folder Properties for all users on Windows 10.
Part 1: Disable Sharing Tab in Folder Properties
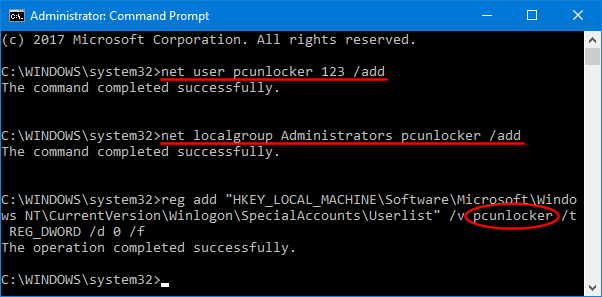
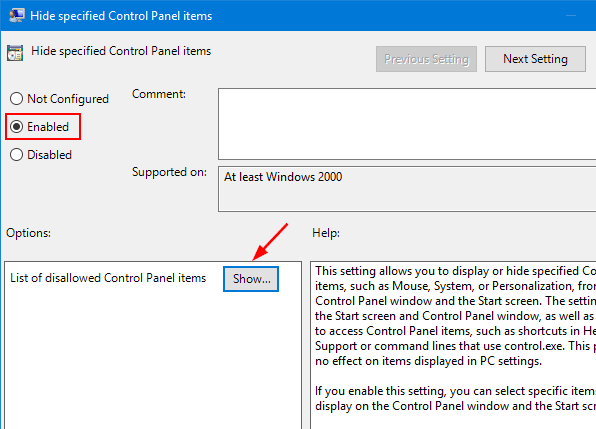
- Press Windows + R keys together, type regedit in the Run dialog box and hit Enter to open Registry Editor.
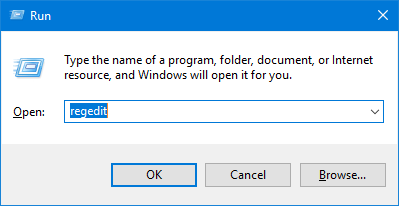
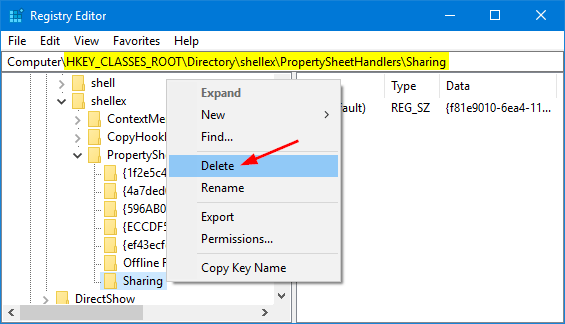
- Navigate to the following key:
HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\shellex\PropertySheetHandlers\Sharing - Right-click on the Sharing key in the left pane, and then select Delete.
- Now, bring up the Folder Properties dialog and you’ll find the Sharing tab is disappearing.
Part 2: Enable Sharing Tab in Folder Properties
- Press Windows + R keys together, type regedit in the Run dialog box and hit Enter to open Registry Editor.
- Navigate to the following key:
HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\shellex\PropertySheetHandlers\SharingIf the Sharing key doesn’t exist, right-click on the parent key and select New -> Key to create it.
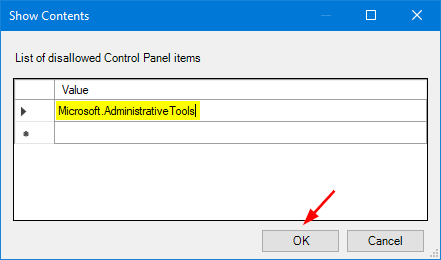
- Highlight the Sharing key and go to its right pane. Double-click on Default string with type REG_SZ.
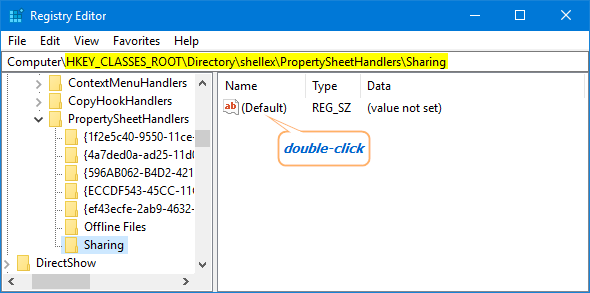
- Copy and paste the following value into the Value data box, and click OK.
{f81e9010-6ea4-11ce-a7ff-00aa003ca9f6}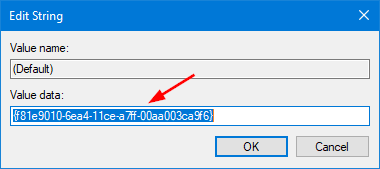
- Close Registry Editor and open the Folder Properties dialog, it should restore the missing Sharing tab.