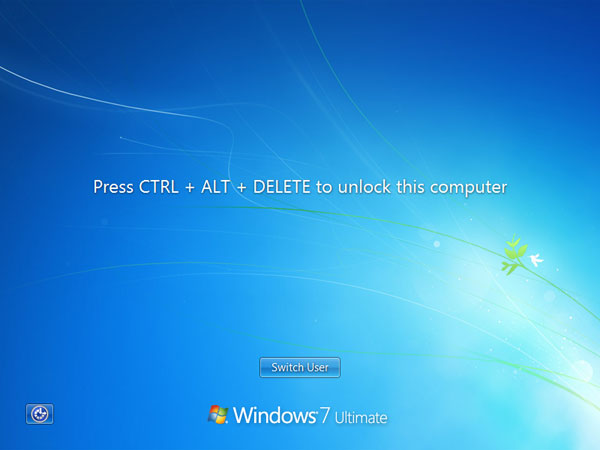
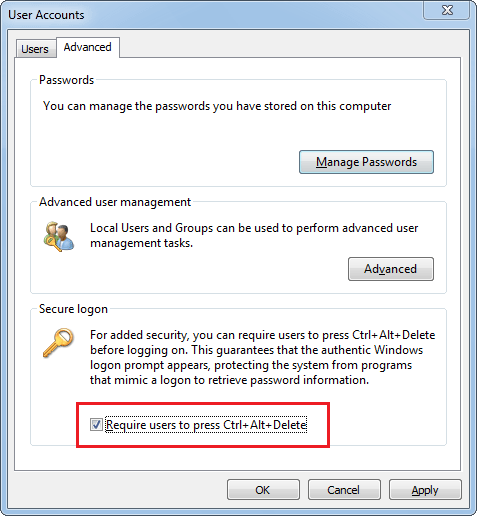
It’s a common security practice to lock your Windows desktop screen by pressing Windows + L keys every time you walk away from your computer. This can prevent other people from accessing your computer in your absence. However, did you realize that Windows will display the user name on the screen while your PC is locked? A user name can be just as sensitive as a password in a lot of scenarios. Luckily there is a simple way to hide your user name from Windows lock screen.
How to Hide User Name from Windows Lock Screen?
- Open the Registry Editor by pressing Windows + R keys simultaneously.
- Browse down to the following registry key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System - On the right-hand side, create a new DWORD 32-bit value named
DontDisplayLockedUserIdand give it one of these values:- 1 = User display name, domain and user names
- 2 = User display name only
- 3 = Do not display user information
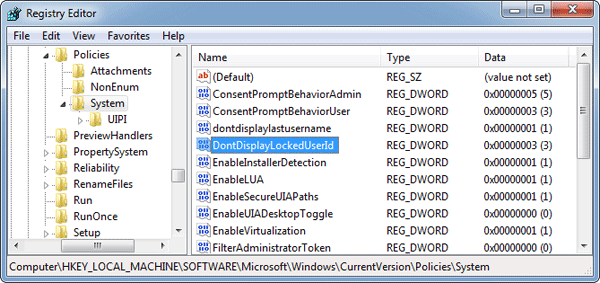
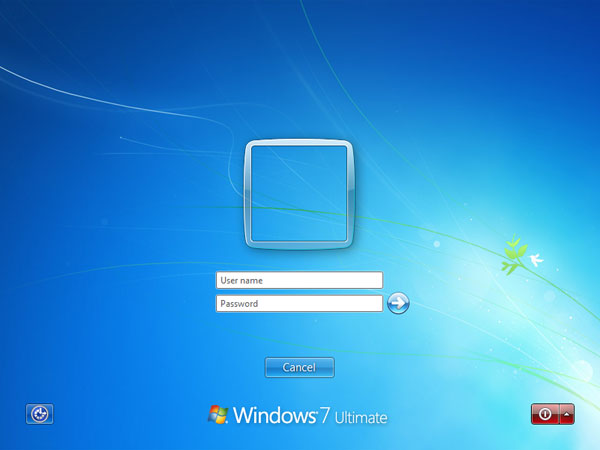
If you change this value to 3 then it will remove all user information from your Windows lock screen.
Note: To prevent the last logged on user to be displayed in the Windows logon screen, also set the dontdisplaylastusername value to 1.
- Exit Registry Editor and reboot your computer. The next time you press Windows + L to lock your computer, your user name will not be displayed on the Windows lock screen any longer. User will be required to enter both their user name and password when logging back in from the locked workstation.
This is how it looks like on a Windows 7 machine.
Before:
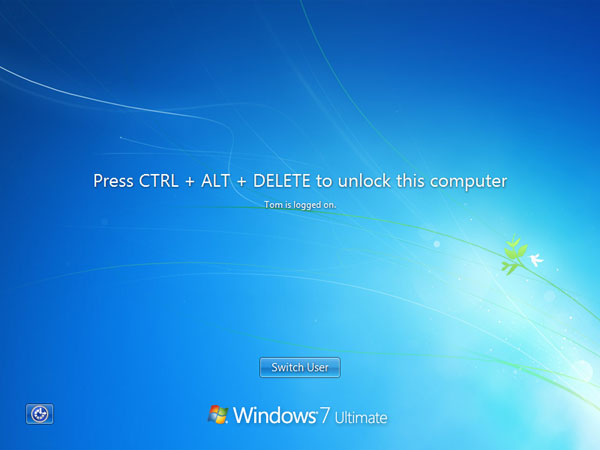
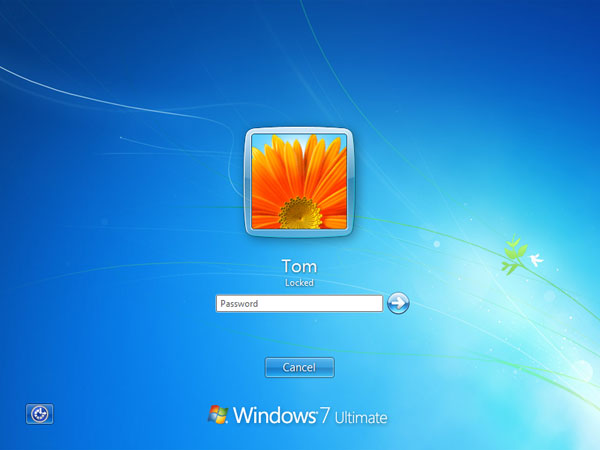
After: