How to view users logon activity in Windows? Do you need to know the time of the last login? In this tutorial we’ll show you how to deploy a GPO in Windows to display information about previous logons during user logon. This feature works on all computers running Windows 10/8/7, Windows Server2008 or later.
Method 1: Show Previous Logon Information with Group Policy Editor
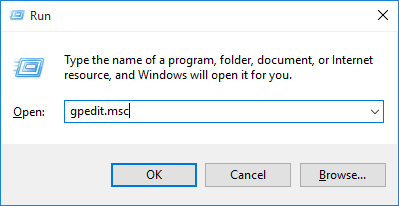
- Press the Windows key + R to open the Run command box. Type gpedit.msc and press Enter.
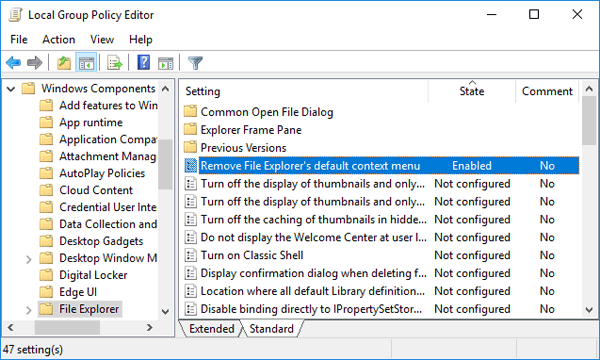
- In the Local Group Policy Editor, drill down to Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Windows Logon Options.
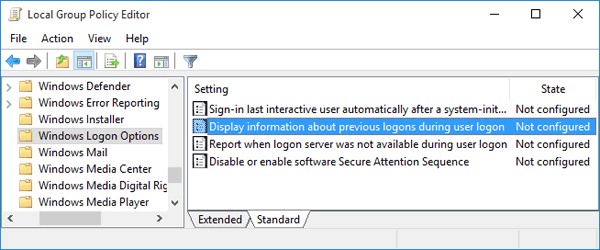
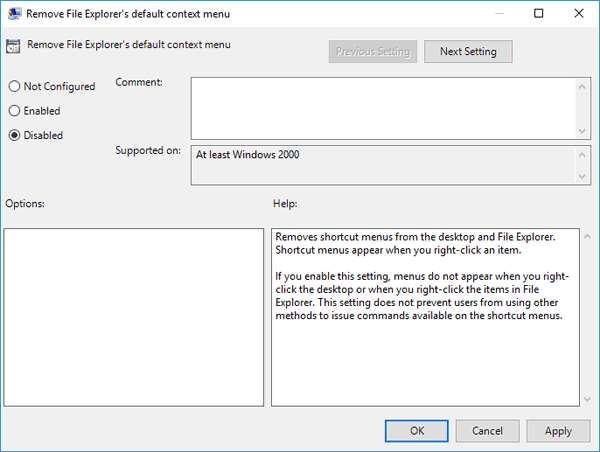
On the right panel, find the “Display information about previous logons during user logon” policy and double-click it.
- Select the Enabled option. Click OK and restart your computer.
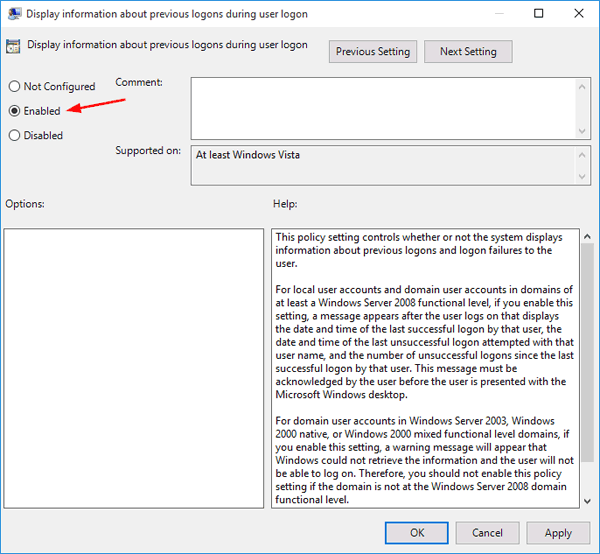
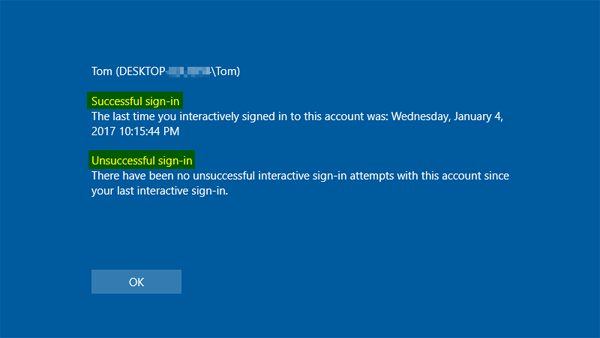
- The next time you log into Windows, after entering your password, you will see the following screen that shows you the time of last successful logon and unsuccessful logon attempts. Click OK and it takes you to the desktop.
Method 2: Show Previous Logon Information with Registry Hack
If you have a Windows Home edition, you need to use the following registry hack to enable the “Display information about previous logons during user logon” policy on your computer.
- Press the Windows key + R to open the Run box. Type regedit and press Enter.
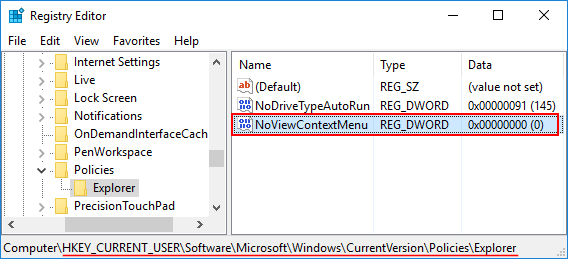
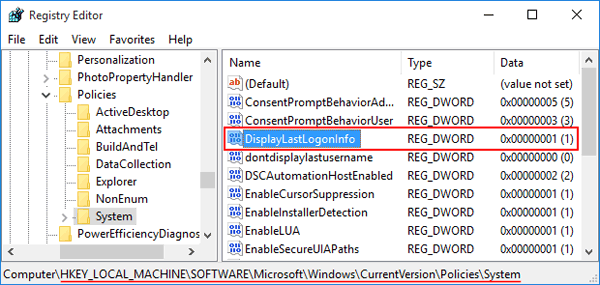
- When the Registry Editor opens, navigate to the following key:
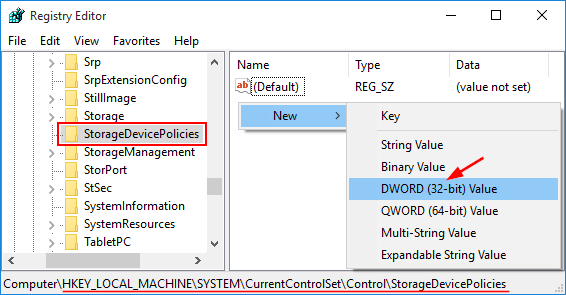
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System - Look for the REG_DWORD value DisplayLastLogonInfo in the right panel. If it doesn’t exist, right-click the empty space and choose New > DWORD (32-bit) Value. Name the new value DisplayLastLogonInfo.
- Double-click DisplayLastLogonInfo and then change the value from 0 to 1. Click OK. (If you don’t want Windows to show previous logon information after sign-in, just change the DisplayLastLogonInfo value back to 0)
- Close Registry Editor and restart your computer. The next time you log into your Windows account it will display last interactive logon information on the welcome screen.