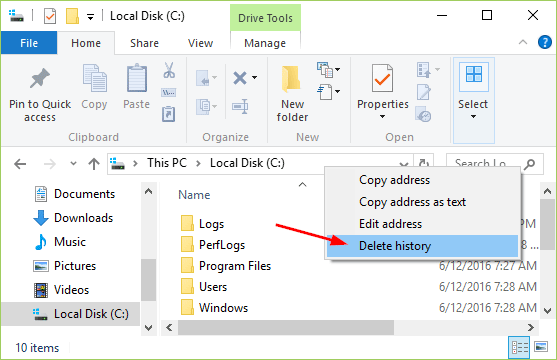
It’s a good idea to put Windows in the energy-saving mode (Sleep or Hibernate) when you’re away from your computer. However, most of users don’t know the exact differences between Sleep mode and Hibernate mode. In this article we’ll try to explain the differences in detail.
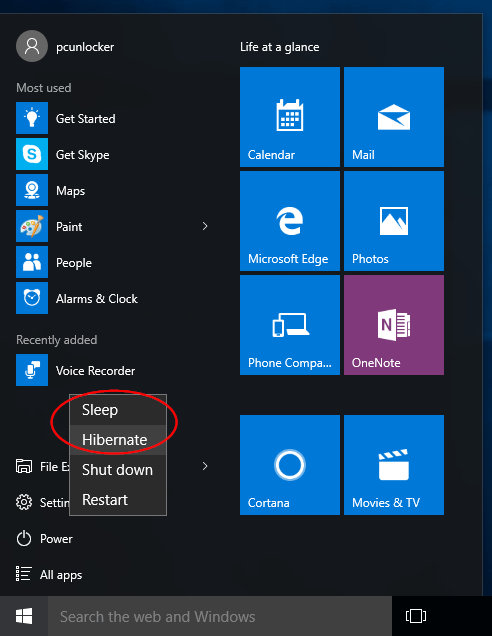
Sleep:
Sleep mode (also known as Standby mode) is useful when you’re going to be away for a short period of time. It’s similar like pausing a DVD movie, all your running programs are suspended. The computer immediately stops most system operations and your open documents and applications are put in the RAM. Power is cut from all components apart from RAM: the display, the hard drive, and ports.
However, the power must NOT be cut off while your PC is in Sleep mode, and must be continue to supply to the computer. A power outage would cause all data that aren’t saved to hard disk to be lost.
When you wake the computer up, all processes and programs resume working within seconds. This is because your computer is still on and all your data is still kept in the computer’s memory.
Hibernate:
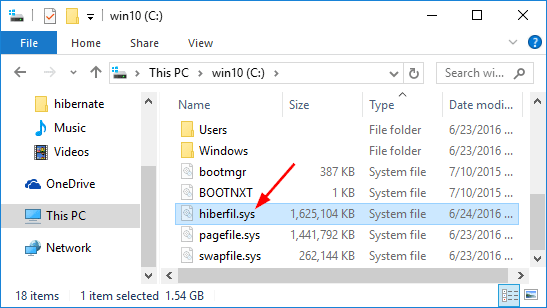
Hibernate mode will take everything you have running on RAM (including open documents and apps) and saves it to a special file (C:\hiberfil.sys) on your hard drive, and then turn off your computer completely. That means it consumes almost no power, but it takes a bit more time to wake up than Sleep mode.
When you wake your computer from hibernation, the system will load everything saved in the hiberfil.sys file and all programs you had open will reopen in the same state you left them.
Hibernation is ideal for users who would be away from the computer for an extended period, especially when you have to cut off the power to travel but want to continue working from where you left off, without having to open your programs and documents again.
The downside of Hibernate is that it will take up a huge amount of disk space because it saves the full memory of the RAM into hard drive, you can see a gigantic hiberfil.sys file sitting in the root of your system drive.
Conclusion
Now you should have found out the main differences between Sleep mode and Hibernate mode. It’s up to you to decide which option is best for you to save power for your computer.